Introduction
Art movements, like vibrant brushstrokes on the canvas of history, have played a pivotal role in shaping the artistic landscape. In this guide, we delve into the kaleidoscope of creative expressions that define various periods. Whether you’re an art enthusiast, student, or professional, understanding these movements unveils a rich tapestry of inspiration and innovation.
What Are Art Movements?
Defining the Essence
Art movements are dynamic rivers in the ever-changing flow of creativity, uniting artists with shared visions. Characteristics vary, but the essence remains – a rebellion, evolution, a response to the zeitgeist.
Examples of Artistic Alchemy
From Impressionists’ brushstrokes capturing fleeting moments to Cubism’s fractured perspectives, each movement is a unique brush dipped in the palette of history. Surrealism’s dreamlike narratives and Abstract Expressionism’s emotional eruptions testify to the diverse tapestry of art movements.
Unraveling the Tapestry of History
Art movements are not isolated chapters but interconnected threads in the grand tapestry of art history. The Renaissance birthed realism, Romanticism embraced emotion, and Modernism challenged tradition. Each movement is a chapter in the ongoing narrative of artistic exploration.
10 Most Famous Art Movements and Styles
Explore the vivid spectrum of art with the 10 most famous art movements and styles. From the emotional eruptions of Abstract Expressionism to the fractured perspectives of Cubism, each movement paints a unique stroke in the canvas of artistic history.
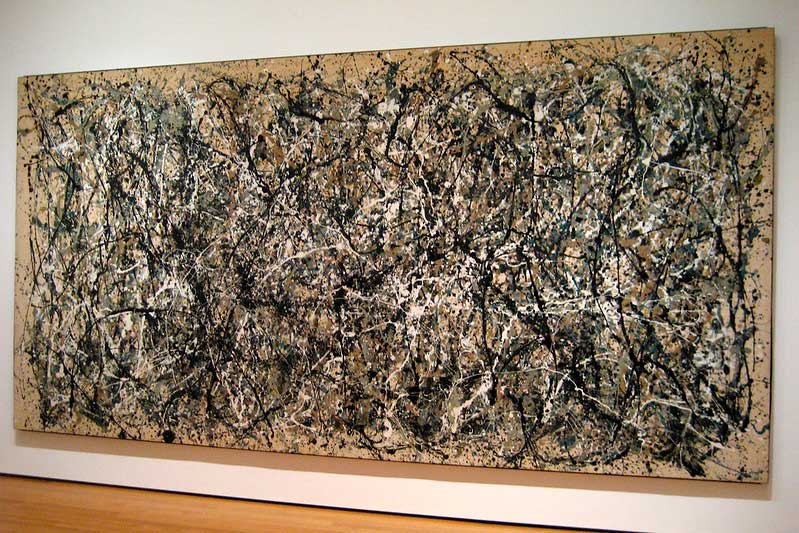


1. Abstract Expressionism
A symphony of emotion, Abstract Expressionism broke the shackles of representation, letting paint dance freely on the canvas. Think Pollock’s rhythmic drips and Rothko’s emotional color fields.
2. Cubism
Picasso and Braque, the pioneers of Cubism, shattered reality into geometric fragments. Faces, landscapes, and objects were deconstructed and reassembled in a revolutionary visual language.
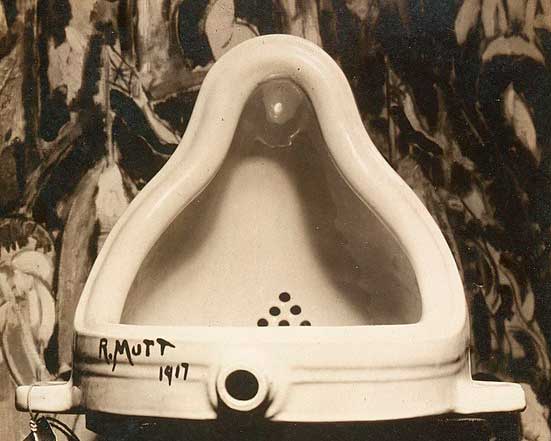
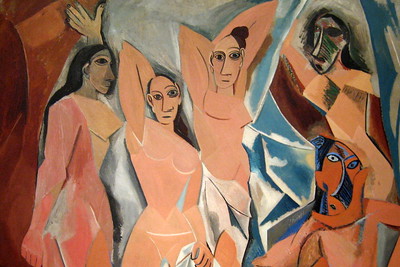
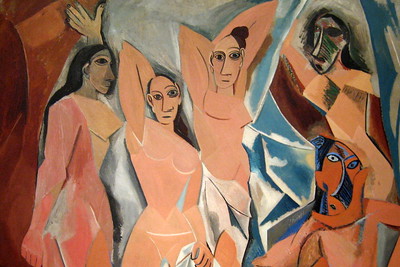


3. Dadaism
Anarchy on canvas, Dadaism embraced chaos, rejecting logic and reason. Duchamp’s ready-mades and absurd performances challenged the very definition of art.
4. Fauvism
A riot of colors, Fauvism celebrated unrestrained expression. Matisse and Derain led the charge, liberating color from its representational duties.
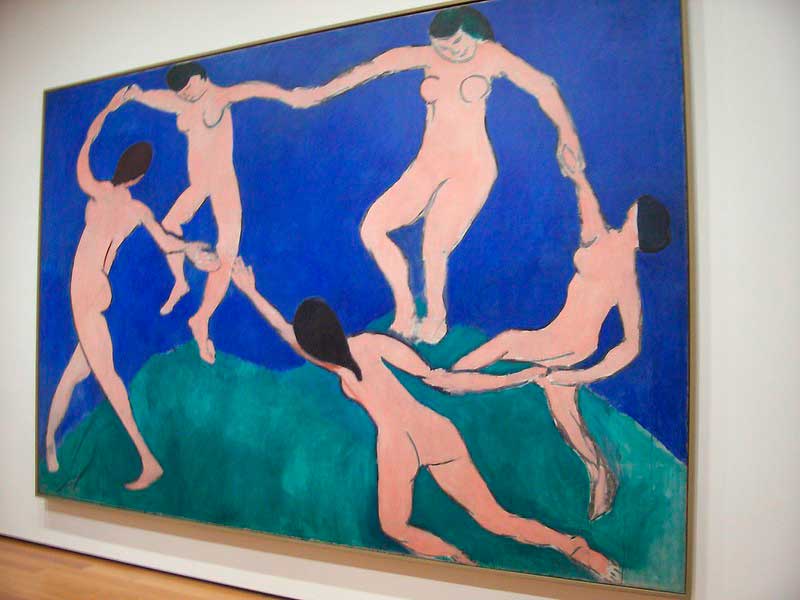
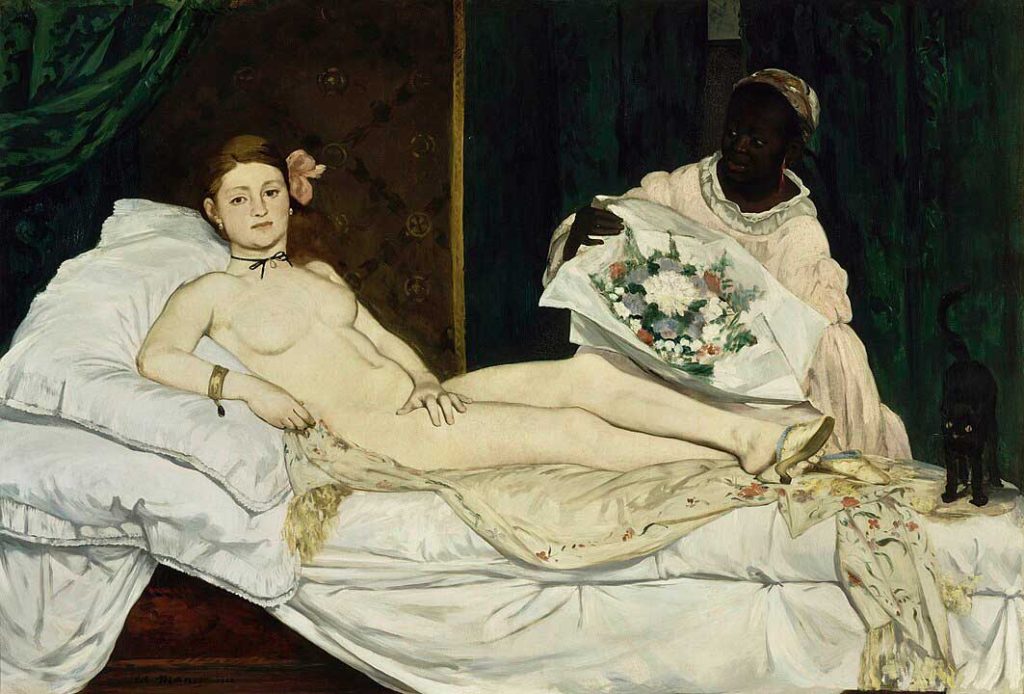




5. Impressionism
Capturing the essence of a moment, Impressionism infused everyday scenes with light and atmosphere. Monet’s water lilies and Renoir’s joyous gatherings epitomize this movement.
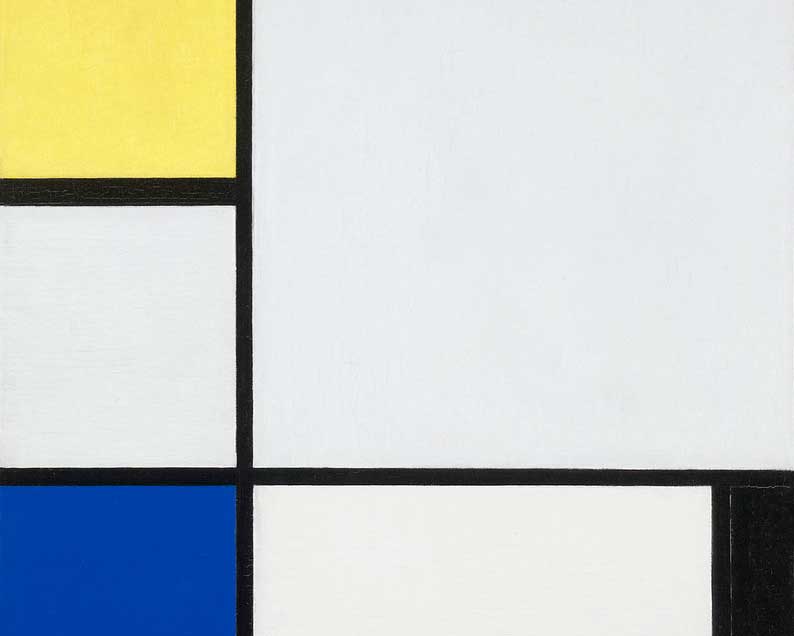
6. Minimalism
Less is more – Minimalism stripped art to its essentials. Stark geometric forms and monochromatic palettes defined a movement that sought beauty in simplicity.



7. Pointillism
Seurat’s meticulous dots defined Pointillism, a technique where tiny dots create a cohesive image from a distance. Precision and patience converged on the canvas.
8. Pop Art
A celebration of consumer culture, Pop Art elevated everyday objects to high art. Warhol’s soup cans and Lichtenstein’s comic-inspired works challenged traditional hierarchies.
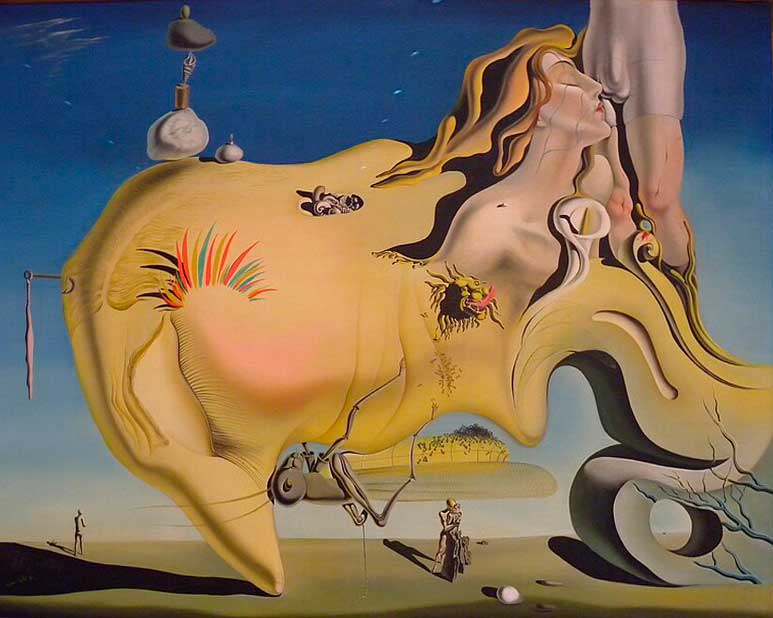




9. Surrealism
Dreams unleashed – Surrealism delved into the subconscious, birthing fantastical landscapes. Dali’s melting clocks and Magritte’s surreal bowler hats defined this enigmatic movement.
10. Symbolism
A poetic rebellion, Symbolism infused art with metaphor and mystery. More than mere representation, artists like Redon and Klimt sought to convey deeper, symbolic truths.


The Evolution of Art Movements: A Dynamic Unfolding of Creativity


Art movements, akin to the ebb and flow of cultural tides, are intrinsically linked to the ever-changing landscapes of society. They don’t exist in a vacuum but evolve in response to the pulsating rhythms of human experience, technology, and prevailing ideologies.
Societal Catalysts: Forging New Perspectives
Art movements often find their roots in the zeitgeist of their time. The Renaissance, for instance, emerged as a response to a renewed interest in classical knowledge, spurred by the rediscovery of ancient texts. Artists sought to emulate the realism of the classical world, marking a departure from the symbolic and stylized depictions of the Middle Ages.
In the Romantic era, industrialization and urbanization brought forth a yearning for nature’s untouched beauty. The movement was a reaction against the mechanization of society, a passionate embrace of emotion, individualism, and the untamed grandeur of the natural world.
Modernism, rising from the ashes of World War I, was a rebellious response to a world shattered by conflict. The traditional conventions of art no longer seemed adequate in conveying the complexity and fragmentation of the modern experience. Artists like Picasso and Duchamp pushed the boundaries, reflecting the disillusionment and radical shifts in perception that characterized the early 20th century.
Technological Advancements: Shaping Artistic Expression
The evolution of art movements is intricately tied to technological advancements. The invention of the camera, for instance, freed artists from the constraints of realistic representation. As photography captured reality with unprecedented accuracy, movements like Impressionism explored new ways of interpreting the world, emphasizing mood and atmosphere over precise details.
The digital age, with its myriad tools and platforms, has given rise to contemporary art movements like Neo-Expressionism and Digital Art. Artists harness technology to explore novel forms of expression, blurring the boundaries between traditional and digital mediums. The evolution of tools and techniques continually reshapes the artistic landscape.
Ideological Shifts: Catalysts for Artistic Rebellion
Art movements are often born out of ideological shifts and a desire to challenge existing norms. Modernism, with its rejection of established traditions, was a response to a world questioning long-standing beliefs. Dadaism, emerging in the aftermath of World War I, rejected logic and reason, mirroring the absurdity of the times.
Political upheavals, social revolutions, and cultural movements all contribute to the evolution of artistic expression. Movements like Pop Art in the 1950s and 1960s, responding to the consumer-driven culture of the time, incorporated everyday objects into high art, challenging the traditional hierarchy of artistic subjects.
Cultural Diversity: Fostering Artistic Pluralism
As the world becomes more interconnected, art movements draw inspiration from a global palette. Movements like Globalism or International Contemporary Art reflect the interconnectedness of diverse cultures. Artists from different corners of the world contribute to a rich tapestry of styles, mediums, and perspectives, fostering a more inclusive and pluralistic artistic landscape.
In essence, the evolution of art movements is a reflection of the human condition. It’s a dynamic interplay between societal influences, technological possibilities, ideological shifts, and the innate human drive to explore, rebel, and create. Each movement, with its distinctive brushstrokes, becomes a chapter in the ongoing narrative of artistic exploration, contributing to the kaleidoscope of human creativity.
Contemporary Art Movements
Embark on a journey through the vibrant palette of contemporary art movements. From the conceptual musings of Conceptual Art to the technological explorations of Ai Art, each movement offers a glimpse into the evolving landscape of modern artistic expression.
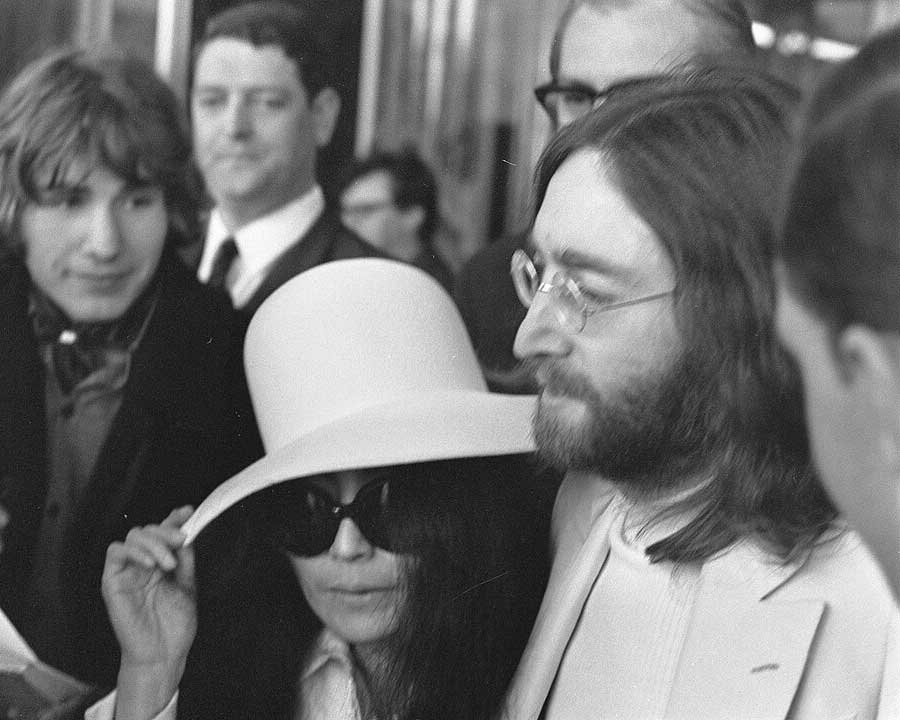


1. Conceptual Art
Ideas over aesthetics – Conceptual Art challenged traditional notions by prioritizing concepts. Think Duchamp’s urinal and Yoko Ono’s conceptual pieces.
2. Photorealism
A nuanced dance with reality, Photorealism blurs the line between painting and photography. Each brushstroke mimics photographic precision, capturing moments with astonishing detail.




3. Fluxus
An avant-garde symphony, Fluxus embraced the experimental. Events, happenings, and performance art defined this movement where art and life intertwined.
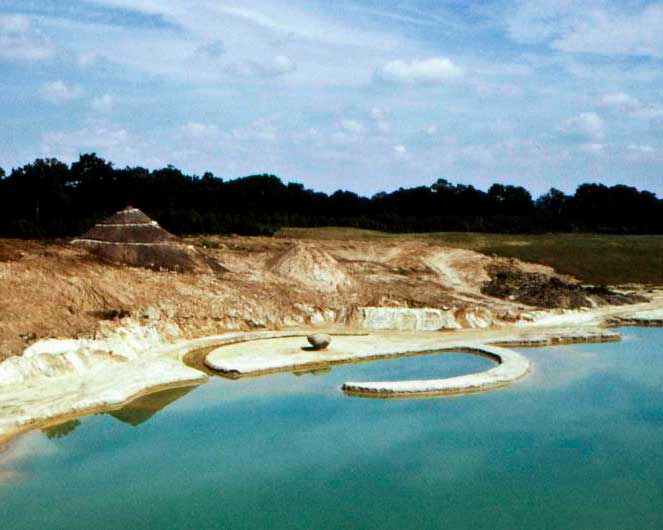
4. Land Art/Earth Art
Art meets nature – Land Art created sculptures from the earth itself. Spiral Jetty by Robert Smithson and Broken Circle by Piet Oudolf are poetic testaments to this movement.




5. Neo-Expressionism
A resurgence of emotion, Neo-Expressionism revived expressive brushstrokes and intense colors. Artists like Basquiat and Schnabel embraced raw, visceral expressions.
6. Text Art
Words as art – Text Art transforms language into visual poetry. From Jenny Holzer’s bold statements to Lawrence Weiner’s conceptual language, it’s a movement that speaks volumes.




7. The Young British Artists
A rebellious wave in British art, YBAs challenged conventions. Hirst’s preserved sharks and Emin’s confessional art marked a bold departure from the traditional.
8. Ai Art
The intersection of art and technology – Ai Art explores the possibilities of artificial intelligence in creative expression. Algorithms become artists in this intriguing movement.
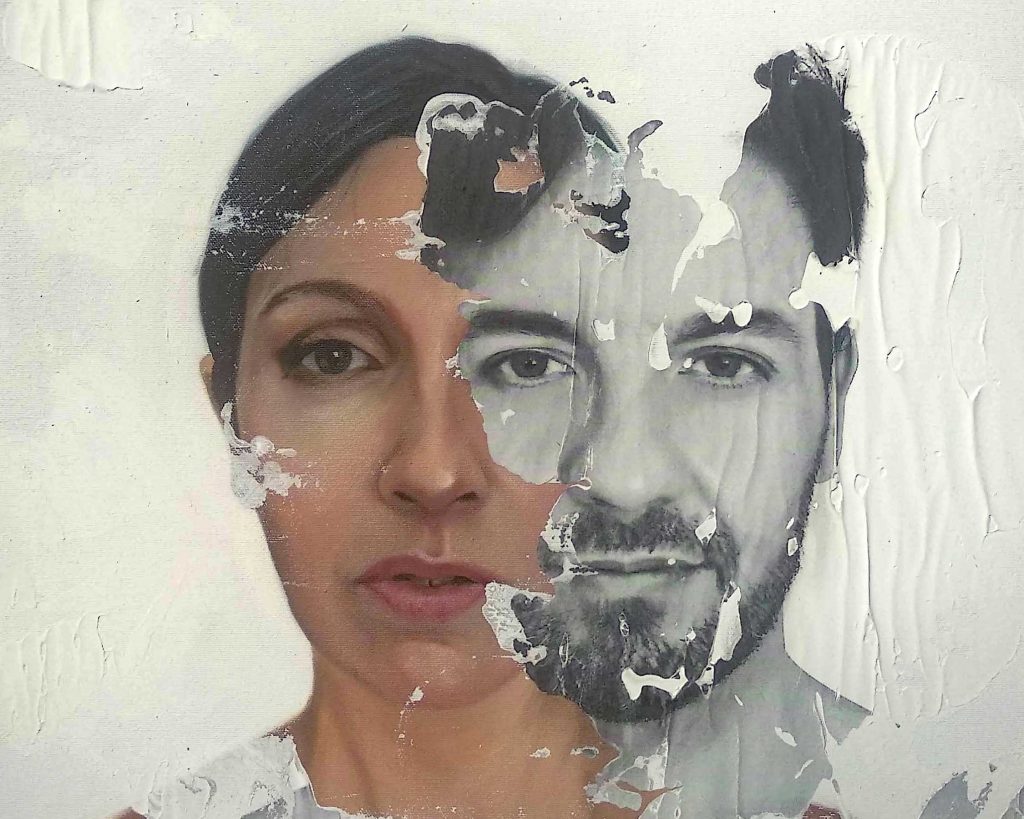




9. Neophotorealism
Blurring the lines between classical painting and image transfer techniques, Neophotorealism is a contemporary dance of traditional and modern artistic elements.
The Impact of Art Movements
Beyond the Canvas
Art movements echo in the corridors of culture, society, and politics. From challenging societal norms to influencing political ideologies, they are cultural seismic shifts that transcend the confines of the gallery.
Cultural Metamorphosis
Art movements are not just aesthetic trends; they are cultural catalysts. The roaring twenties witnessed the rebellion of the Dadaists, mirroring the chaos of a world recovering from war. Pop Art emerged in the consumer-driven frenzy of the 1950s and 1960s, reflecting a society obsessed with mass production and media.
Societal Reflections
From the utopian ideals of the Arts and Crafts Movement to the politically charged murals of the Mexican Muralism movement, art has been a mirror to society. Movements like Surrealism, with its dreamlike imagery, offered an escape during times of war and social upheaval.
Political Narratives
Art has been a silent but powerful political force. From the politically charged posters of the Russian Constructivists to the anti-establishment sentiments of Punk Art, movements have rallied against the status quo, challenging authority and inspiring change.
How to Identify an Art Movement
Decoding the Canvas
Spotting an art movement is like deciphering a visual code. Pay attention to techniques, themes, and context. Knowing the language of art movements adds depth to the viewing experience, turning a canvas into a dialogue with history.
Reading Between the Strokes
Understanding the context is crucial. The Abstract Expressionists, for example, emerged in post-war America, expressing the existential angst of the time. Cubism, born in the early 20th century, reflected the fractured worldview of a world on the brink of change.
Technical Tell-Tales
Brushstrokes, color palette, and composition can be clues. Pointillism’s meticulous dots or the bold colors of Fauvism are distinctive features that set each movement apart.
Historical Context
Art movements are often reactions to historical events. The anti-establishment stance of Dadaism emerged in the aftermath of World War I, questioning the very fabric of society. Understanding the historical backdrop enriches the interpretation of the artwork.
Conclusion
In this artistic odyssey, we’ve traversed the vast landscapes of art movements. Each stroke, each movement, contributes to the symphony of human creativity. Embrace the diversity, explore the nuances, and let the canvas be a portal to worlds unexplored.
FAQs
Q1: Why are art movements important?
Art movements shape artistic evolution, reflecting societal shifts and pushing creative boundaries.
Q2: Can one artwork belong to multiple art movements?
Absolutely. Some artworks defy categorization, embodying the spirit of multiple movements.
Q3: Are art movements relevant in contemporary art?
Yes, they continue to influence contemporary artists, providing a historical context and a platform for innovation.
Q4: How do art movements impact the art market?
Art movements can significantly influence market trends, affecting the value and demand for certain styles.
Q5: Is Neophotorealism a recognized art movement?
Yes, Neophotorealism bridges classical and modern techniques, carving its niche in the contemporary art scene.




