Introduction
Art therapy, a burgeoning field in mental health, has gained significant traction in recent years. As individuals seek holistic approaches to well-being, the transformative power of artistic expression becomes increasingly apparent. In this article, we’ll delve into the realm of art therapy, exploring its various activities, benefits, and the qualifications essential for those guiding individuals on this creative journey.
What is Art Therapy?


Art therapy is more than just creating aesthetically pleasing artwork; it’s a therapeutic process that taps into the expressive nature of art to address emotional and psychological challenges. Through this medium, individuals can communicate, explore, and understand their emotions in a non-verbal way. The canvas becomes a mirror to the soul, revealing insights that might be challenging to articulate otherwise.
Types of Art Therapy Activities
Art therapy encompasses a diverse range of activities. From painting and drawing to sculpting and collage-making, each activity serves as a unique avenue for self-discovery and healing. The choice of activity often depends on an individual’s preferences and the therapeutic goals outlined by the art therapist.
Benefits of Art Therapy
The benefits of engaging in art therapy are manifold, extending beyond the confines of the studio. One of the primary advantages is stress relief; the act of creating art provides a cathartic release, allowing individuals to channel their emotions into a tangible form. Additionally, art treatment fosters improved communication skills, aiding individuals in expressing thoughts and feelings that might be challenging to verbalize.
Furthermore, art therapy promotes increased self-awareness. As individuals engage in the creative process, they gain insights into their emotions, thoughts, and behavioral patterns. This heightened self-awareness is a cornerstone in the journey towards mental and emotional well-being.
Art Therapist
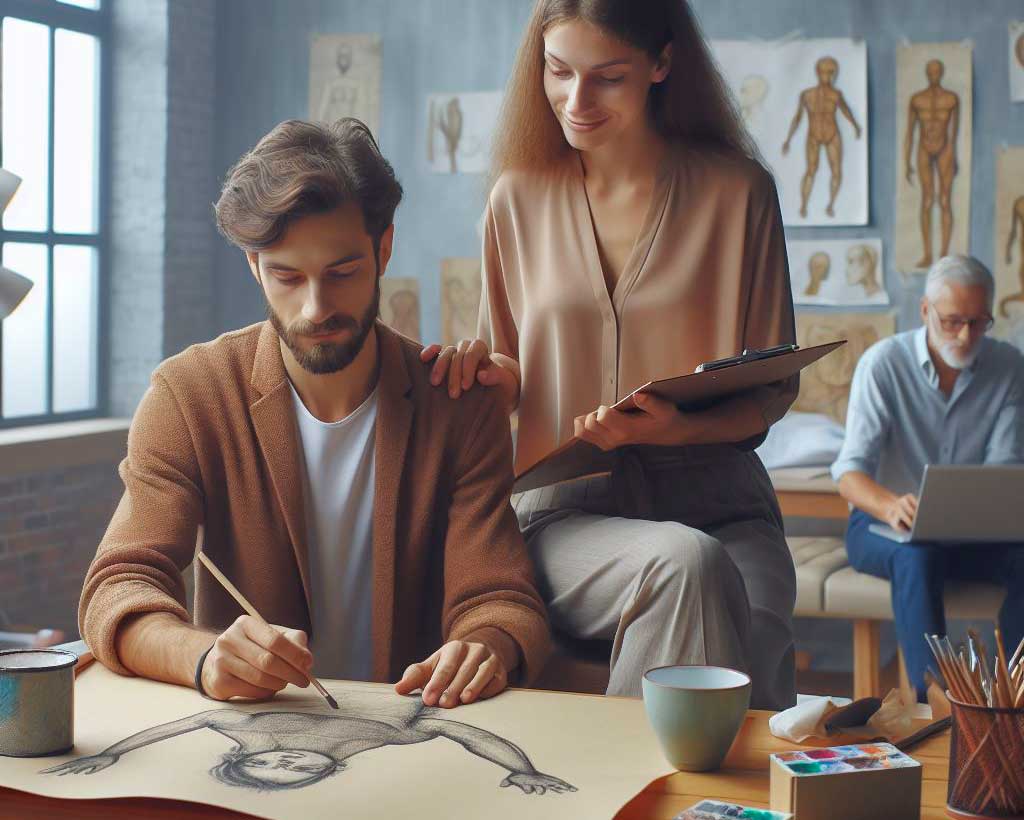


At the heart of art therapy is the art therapist, a professional trained to guide individuals through the creative process. Art therapists work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, schools, rehabilitation centers, and private practices. They facilitate sessions, create a safe space for expression, and interpret the artwork in collaboration with the individuals undergoing therapy.
Art Therapist Qualifications


Becoming an art therapist requires dedication and a specific set of qualifications. A master’s degree in art therapy is a foundational requirement, equipping therapists with the theoretical and practical knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the human psyche through art.
Essential Skills and Qualities
In addition to formal education, art therapists must possess certain skills and qualities. Empathy is paramount, as it allows therapists to connect with their clients on a deep emotional level. Creativity is another essential trait, enabling therapists to adapt to the diverse needs and preferences of their clients. Good communication skills are vital, fostering a collaborative and supportive therapeutic relationship.
Types of Art Therapy
Art therapy encompasses a rich tapestry of approaches, each designed to cater to specific therapeutic objectives. Let’s explore additional types that further enrich the spectrum of art therapy:
Jungian Art Therapy
Rooted in the principles of Carl Jung’s analytical psychology, Jungian Art Therapy delves into the exploration of archetypes, symbols, and the collective unconscious. This approach encourages individuals to tap into universal symbols, fostering a deeper understanding of their inner selves and connecting with broader human experiences.
Dance/Movement Therapy
While not strictly confined to visual arts, dance/movement therapy is a dynamic form of expressive therapy. It harnesses the physicality of movement as a means of self-expression. Through dance and movement, individuals can embody and externalize their emotions, promoting a holistic integration of mind and body in the therapeutic process.
Music Therapy
Incorporating auditory and rhythmic elements, music therapy extends the expressive potential beyond visual arts. Individuals engage in creating music or using existing compositions to evoke emotions and explore their inner landscapes. The rhythmic and melodic aspects of music can be particularly powerful in facilitating emotional expression and self-discovery.
Phototherapy
Utilizing photography as a medium for self-expression, phototherapy invites individuals to capture images that resonate with their emotions or experiences. The selected photographs become a visual narrative, allowing for reflection and exploration of personal themes. This visual storytelling aspect can be a potent tool for those who find comfort and expression through the lens.
Eco-Art Therapy
In a world increasingly disconnected from nature, eco-art therapy seeks to reintegrate individuals with the natural environment. This approach involves creating art in natural settings, using natural materials. The process emphasizes the interconnectedness between artistic expression and the broader ecological context, fostering a sense of harmony and balance.
Digital Art Therapy
In our technologically driven age, digital art therapy harnesses the power of digital tools and platforms for creative expression. Individuals can explore various digital mediums, from graphic design to digital painting, providing an alternative and accessible means of artistic expression. This form of art therapy is particularly relevant for those comfortable with technology or seeking innovative modes of creativity.
Drama Therapy
Engaging individuals in theatrical activities, drama therapy explores the therapeutic potential of dramatic expression. Through role-playing, improvisation, and storytelling, individuals can embody different aspects of themselves, enabling a deeper understanding and integration of their emotions. Drama therapy often proves effective in breaking down emotional barriers and fostering cathartic release.
Expressive Arts Therapy
As an integrative approach, expressive arts therapy combines multiple creative modalities, such as visual arts, movement, music, and drama. This holistic approach allows individuals to choose the artistic forms that resonate most with them, creating a personalized and comprehensive therapeutic experience that addresses various facets of their emotional and psychological well-being.
In conclusion, the realm of art therapy is expansive, offering a diverse array of approaches to suit the unique needs and preferences of individuals. Each type of art treatment serves as a doorway to self-discovery and healing, inviting individuals to embark on a transformative journey through the expressive language of art. Whether through visual arts, movement, music, or digital mediums, the therapeutic power of artistic expression knows no bounds.
How Art Therapy Works


Art therapy operates on the principle that artistic expression serves as a powerful tool for individuals to communicate and process complex emotions. The process of creating art in a therapeutic setting goes beyond the aesthetic outcome; it involves a deep exploration of one’s inner world, fostering self-discovery and emotional healing.
Expressive Nature of Art
At the core of how art therapy works lies the expressive nature of art itself. When engaging in artistic activities, individuals can convey thoughts, feelings, and experiences without relying solely on verbal communication. This non-verbal approach is particularly beneficial for those who find it challenging to articulate their emotions through words.
Cathartic Release
The act of creating art provides a cathartic release, allowing individuals to externalize and make sense of their emotions. Whether it’s through the strokes of a paintbrush, the molding of clay, or the arrangement of colors in a collage, the creative process becomes a channel for channeling and processing feelings of stress, anxiety, or even trauma.
Symbolic Representation
Art therapy often involves the use of symbolism in the created artwork. Colors, shapes, and images can carry personal meanings that may not be immediately apparent. The art therapist collaborates with the individual to unravel these symbols, facilitating a dialogue that enhances self-awareness and insight into subconscious thoughts and feelings.
Therapeutic Relationship
Central to the effectiveness of art treatment is the therapeutic relationship between the individual and the art therapist. The therapist creates a safe and non-judgmental space for expression, encouraging the individual to explore their creativity freely. This supportive environment fosters trust and openness, allowing for a deeper exploration of emotions and experiences.
Integration of Mindfulness
Some forms of art therapy, such as Mindfulness-Based Therapy, incorporate mindfulness techniques into the creative process. This integration enhances self-awareness, encouraging individuals to be fully present in the moment as they engage with the artistic medium. Mindful creation promotes a sense of calm and focus, contributing to the overall therapeutic experience.
Personal Empowerment
Art therapy works by empowering individuals to take an active role in their healing journey. Through the act of creation, individuals gain a sense of agency and control over their emotions. This empowerment extends beyond the studio, positively influencing how individuals navigate challenges in their daily lives.
In essence, art therapy works by providing a unique and personalized avenue for individuals to explore, express, and understand their emotions. The combination of creative expression, therapeutic guidance, and a supportive environment creates a transformative space where healing can flourish. Through the language of art, individuals embark on a journey of self-discovery, unlocking the potential for profound emotional and mental well-being.
How to Get Started with Art Therapy
Embarking on an art therapy journey can be a transformative experience. To get started, consider the following tips:
- Explore Your Preferences: Experiment with different art forms to discover what resonates with you.
- Create a Safe Space: Establish a dedicated and comfortable space for your creative endeavors.
- Start Small: Begin with simple art activities and gradually explore more complex projects.
- Express Without Judgment: Remember, there’s no right or wrong in art therapy; it’s about the process, not the end result.
- Consider Professional Guidance: If needed, seek the expertise of a qualified art therapist to guide you through the therapeutic process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, art therapy stands as a powerful modality for self-discovery and healing. Whether you’re navigating stress, seeking improved communication, or aiming for increased self-awareness, the expressive nature of art can be your ally on this journey towards mental and emotional well-being. By embracing the creative process, individuals not only create art but also craft a pathway to understanding and embracing the nuances of their inner worlds. Art treatment opens doors to self-reflection, empowerment, and the profound realization that healing can be a masterpiece in progress.
FAQs
1. What is the role of an art therapist?
Art therapists guide individuals through the creative process, creating a safe space for expression and interpreting artwork collaboratively with clients to address emotional and psychological challenges.
2. Can anyone benefit from art therapy?
Yes, art therapy is inclusive and can benefit individuals of all ages and backgrounds. It is particularly effective for those seeking alternative forms of expression or facing challenges in verbal communication.
3. Are there specific qualifications needed to become an art therapist?
Yes, a master’s degree in art therapy is typically required. Additionally, art therapists should possess essential skills such as empathy, creativity, and good communication abilities.
4. How do different types of art therapy differ from each other?
Various types of art therapies, such as Gestalt and Narrative Art Therapy, focus on different aspects of the therapeutic process. They employ distinct approaches to achieve specific therapeutic goals.
5. Can I practice art therapy on my own at home?
Absolutely. Many individuals engage in art therapy independently at home. Creating a dedicated and comfortable space, experimenting with different art forms, and expressing without judgment are key elements in this self-guided journey.