Introduction
The creative process is a complex and often misunderstood phenomenon. It is the process by which ideas are generated, developed, and transformed into tangible products or outcomes. In the context of an art website, the creative process is of utmost importance as it is the foundation upon which all artistic endeavors are built. In this article, we will explore the creative process in detail and provide insights on how to optimize it for maximum creativity.
Key Takeaways
- The creative process is a non-linear and iterative process that involves ideation, experimentation, and refinement.
- The creative process can be broken down into four stages: preparation, incubation, illumination, and verification.
- Creativity is not limited to artists and designers; it is a skill that can be developed and applied in various fields.
What is the Creative Process?
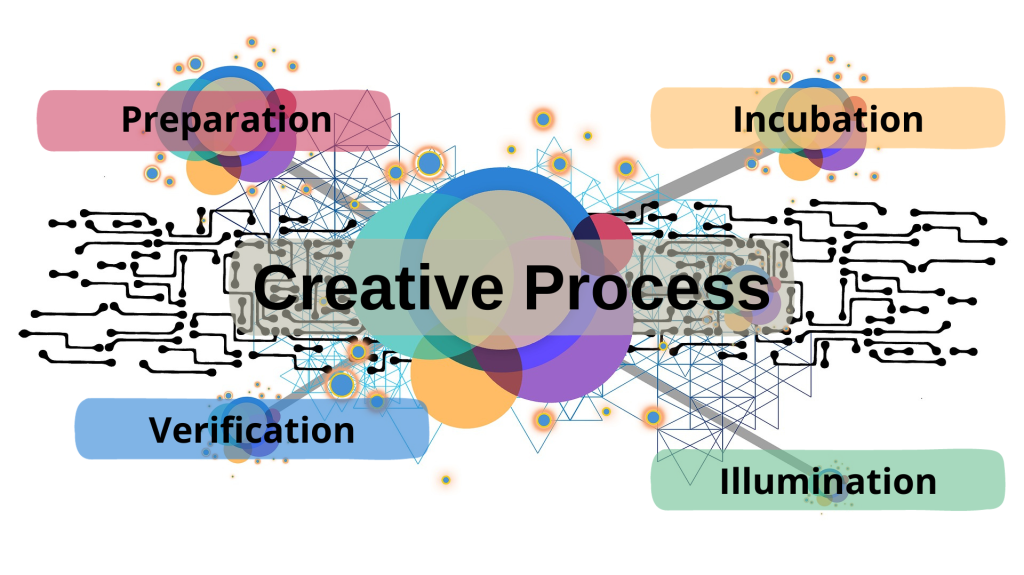

The creative process is a non-linear and iterative process that involves ideation, experimentation, and refinement. It is a journey that begins with an idea or a problem and ends with a solution or a product. The creative process can be broken down into four stages: preparation, incubation, illumination, and verification.
Preparation:
This stage involves gathering information, researching, and brainstorming ideas. It is the stage where you define the problem or the idea that you want to work on. This stage is crucial as it sets the foundation for the rest of the creative process.
Incubation:
This stage involves letting your mind wander and allowing your subconscious to work on the problem or idea. It is the stage where you take a break from actively thinking about the problem or idea and allow your mind to rest.
Illumination:
This stage involves having an “aha” moment where you come up with a breakthrough idea or solution. It is the stage where your subconscious mind presents you with a solution that you may not have thought of before.
Verification:
This stage involves testing and refining your idea or solution. It is the stage where you evaluate your idea or solution against your original problem or idea.
Optimizing the Creative Process
The following are some tips for optimizing the creative process:
Embrace Failure:
Failure is more than a stumbling block; it’s a stepping stone to innovation. Embrace each setback as a unique lesson in your creative journey. Recognize that even the most renowned creators faced failures before achieving their masterpieces. This mindset shift transforms failure from an obstacle into a powerful catalyst for growth, pushing you to iterate, refine, and ultimately, succeed.
Collaborate:
The magic of collaboration lies not just in the amalgamation of ideas but in the diversity of thought that it brings. Engaging with others cultivates a rich tapestry of perspectives, creating a dynamic synergy that propels creativity to new heights. Embrace collaborative spaces as crucibles of innovation, where the fusion of minds ignites a spark that can illuminate unexplored creative territories.
Take Breaks:
In the world of creativity, pauses are not interruptions; they are strategic interludes. Taking breaks is not just about physical rest but a mental reset. Stepping away from your work momentarily allows your subconscious to continue problem-solving in the background. These intervals become fertile ground for unexpected insights, ensuring that your creative well remains deep and consistently replenished.
Experiment:
The essence of creativity lies in the freedom to explore the unknown. Experimentation is your playground, where you test the boundaries of conventional thinking. Don’t view experiments as mere trials; see them as daring adventures into uncharted territories. Each experiment, successful or not, contributes to the evolution of your creative process, shaping a distinctive path towards innovation.
Stay Curious:
Curiosity is not just an initial spark but a perpetual flame that fuels the creative engine. Cultivate an insatiable appetite for knowledge and discovery. Dive into realms unrelated to your immediate focus; let the tangential allure of curiosity introduce unexpected elements into your creative process. In this perpetual state of wonder, you’ll find the seeds of inspiration that germinate into groundbreaking creative endeavors.
The Creative Process in a Painting


The Journey Begins: From Idea to Sketch
Ideation – The Birth of Ideas
In the vast landscape of creativity, ideation stands as the genesis—an exploration of the uncharted realms of imagination. Artists dive into the sea of possibilities, capturing fragments of inspiration that spark the birth of an idea.
Crafting Ideas Into Form
Ideas, once conceived, demand refinement. Artists mold their thoughts, sculpting them into coherent shapes. This phase requires a delicate balance between intuition and intention, as the artist strives to breathe substance into the intangible.
The Importance of Sketching
Sketching, the preliminary dance of the artist’s hand on paper, plays a pivotal role. It is the visual manifestation of an idea, a roadmap guiding the artist through the creative landscape. Sketching not only solidifies concepts but also serves as a playground for experimentation.
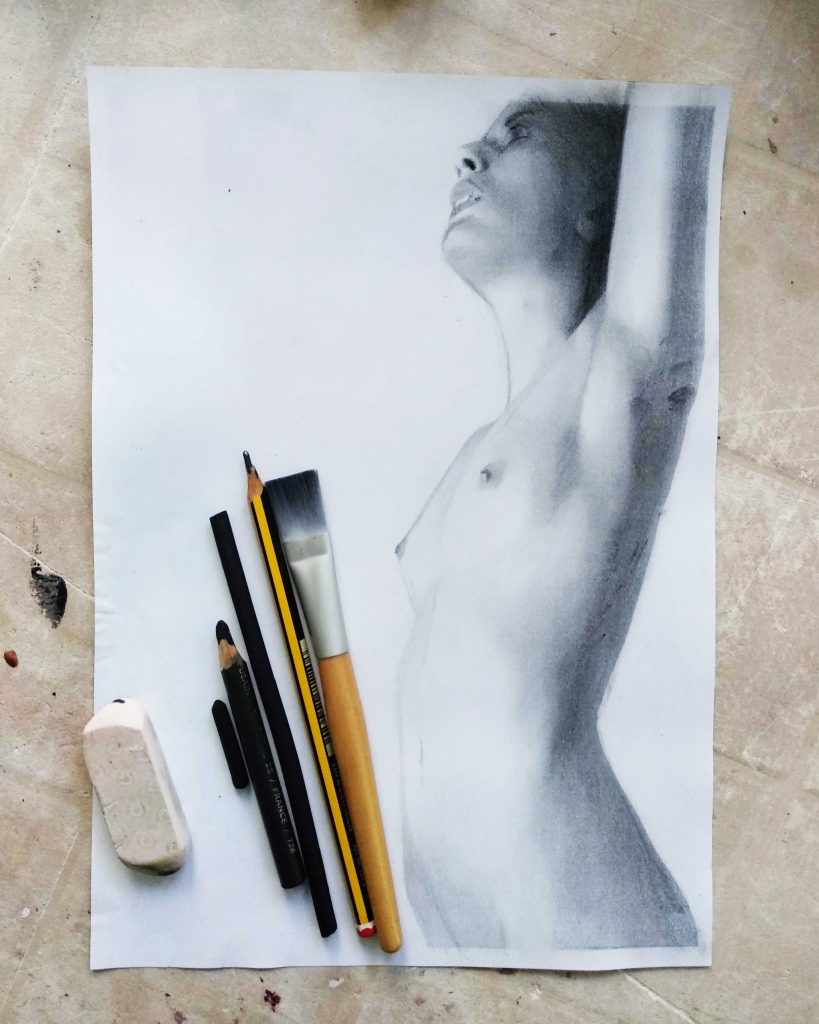


The Evolution of an Idea: From Sketch to Drawing
Conceptualization – Breathing Life Into Sketches
As ideas take form in sketches, the journey transcends to the conceptualization stage. Artists refine their sketches, infusing them with depth and detail. This phase is marked by the fusion of artistic intuition and constructive criticism.
Harnessing the Power of Feedback
In the crucible of creativity, feedback emerges as a catalyst for growth. Artists open themselves to constructive critique, using it as a tool to hone their craft. Feedback is the compass guiding the artist, ensuring the journey stays true to the intended destination.
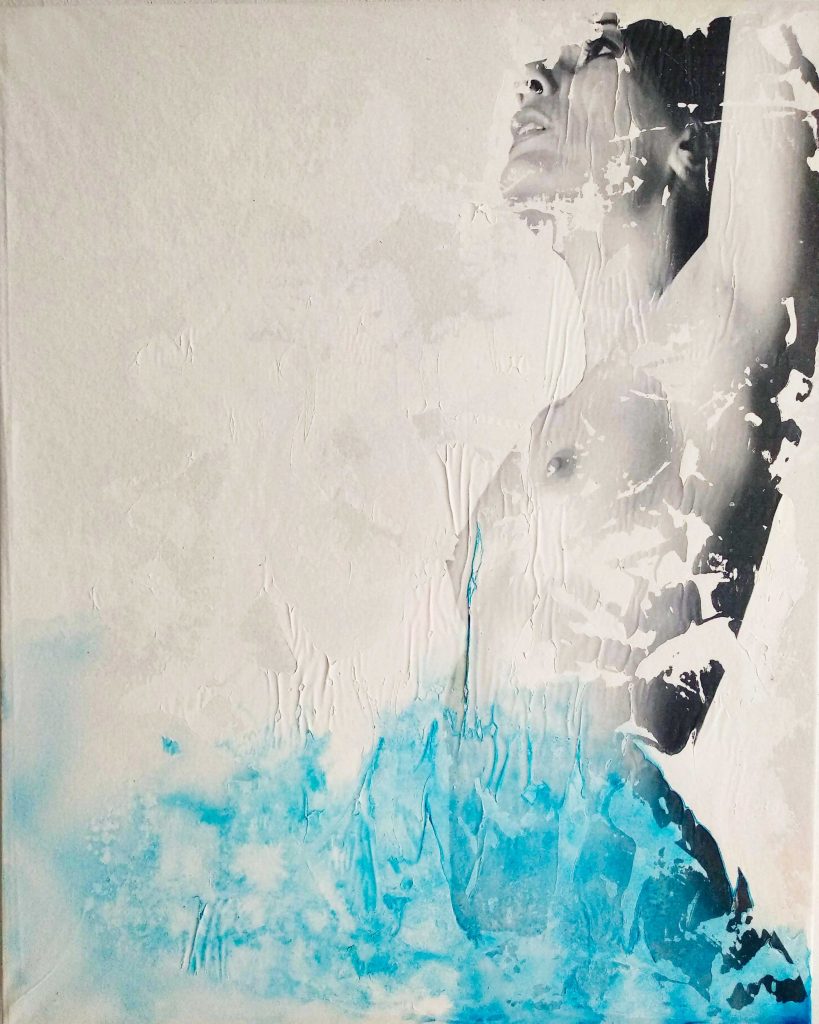


Bringing the Idea to Life: From Drawing to Painting
Execution – The Artistic Alchemy
The execution stage is the alchemical transformation of drawings into vibrant paintings. Artists, armed with a palette of colors and a symphony of brushes, breathe life into their creations. This phase is a dance of technique and expression, where experimentation takes center stage.
Embracing the Dance of Experimentation
Experimentation is the heartbeat of creativity. Artists push boundaries, testing the limits of their medium. It is in the realm of experimentation that mistakes become stepping stones, and unexpected discoveries shape the final narrative of the artwork.


The Finished Masterpiece: From Painting to Exhibition
Presentation – Unveiling the Magnum Opus
The final act of the creative process is presentation—an art in itself. Artists prepare their works for exhibition, curating an experience for the audience. The journey culminates in the public unveiling of the masterpiece, where the artist’s vision meets the spectator’s gaze.
The Ongoing Dialogue of Feedback
Even as the artwork adorns the walls of galleries, the dialogue persists. Feedback from viewers becomes a mirror reflecting the impact of the masterpiece. Artists, ever-evolving, use this feedback to refine their approach and embark on new creative journeys.
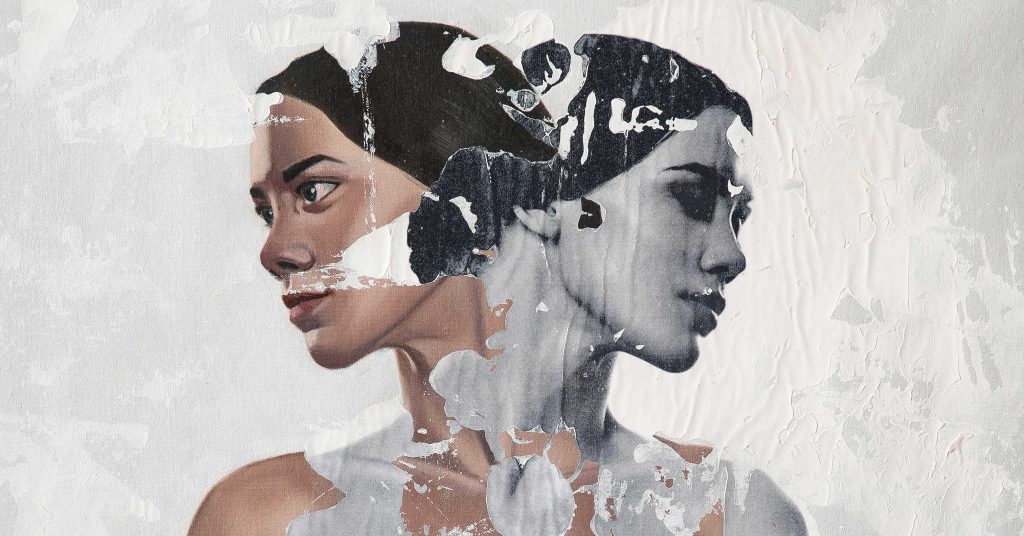
The Creative Process in Neophotorealism Style
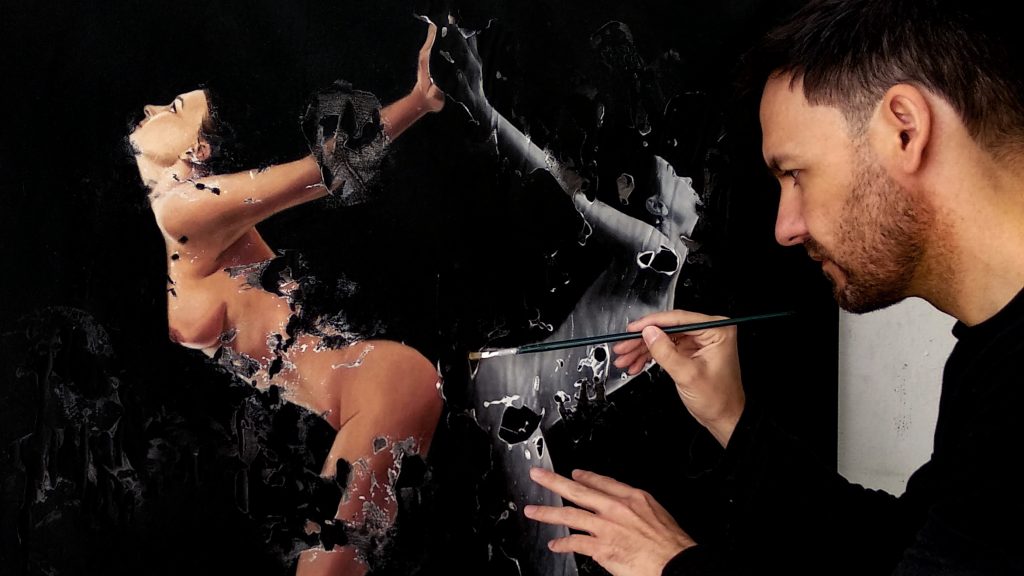


Neophotorealism is a new and unique artistic technique created and developed by Raúl Lara that combines the use of photography through image transfer, and traditional realistic oil painting to create a new form of figurative expressionism. The following are the steps involved in the creative process for neophotorealism style:
Inspiration:
The first step in the creative process is finding inspiration. This can come usually comes mainly from emotional feelings. For Raúl Lara´s neophotorealism style, the principal motivation is to capture the essence of human being.
Composition:
The composition of these paintings is meticulously crafted through digital techniques, harnessing the capabilities of programs like Photoshop to achieve the ideal juxtaposition of two integral elements: the hand-painted image and its transfer onto the canvas.
Painting:
Once the composition is clear and complete, the artist begins painting using traditional realistic oil painting techniques . This involves layering oil paint to create depth and texture.
Image Transfer:
Once the painting is complelety dry, the process of image transfer begins. This involves transferring an image onto canvas using gesso Gesso is a white paint mixture consisting of a binder mixed with chalk, gypsum, pigment, or any combination of these.
Finishing Touches:
The final step in the creative process is adding finishing touches to the painting. This can include adding highlights or shadows to create contrast and depth to the figure painted or even to the transferred.
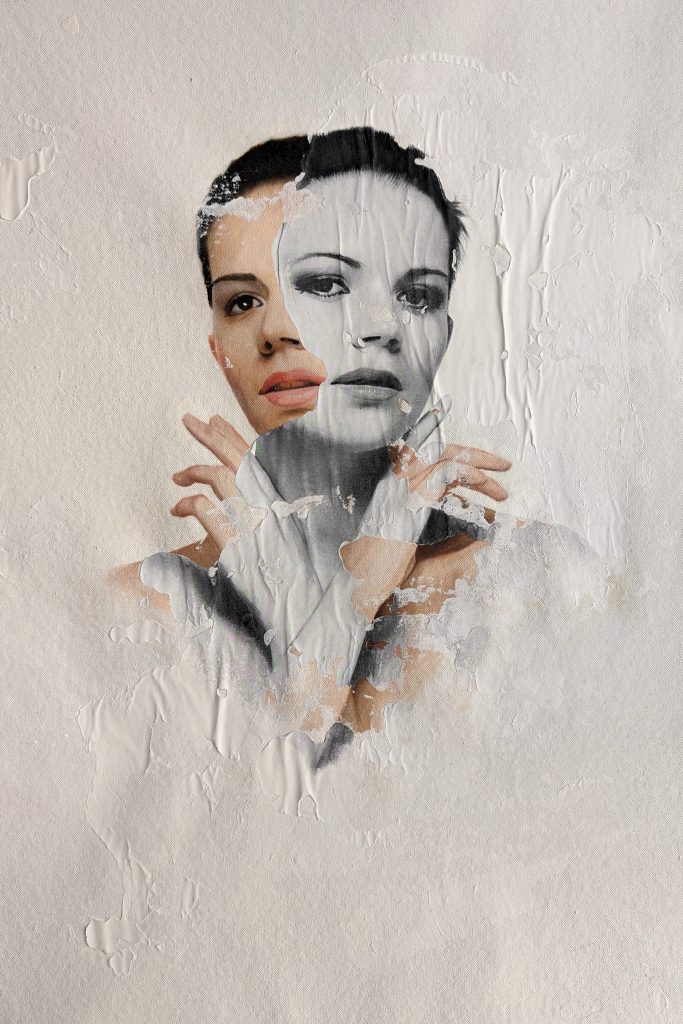
Examples of Neophotorealism Style
Raúl Lara is an artist who has mastered neophotorealism style 1. His works showcase the unique elements of this technique such as color, texture, and the representation of the female figure as a symbol of human purity . Here are some examples of Raúl´s work:
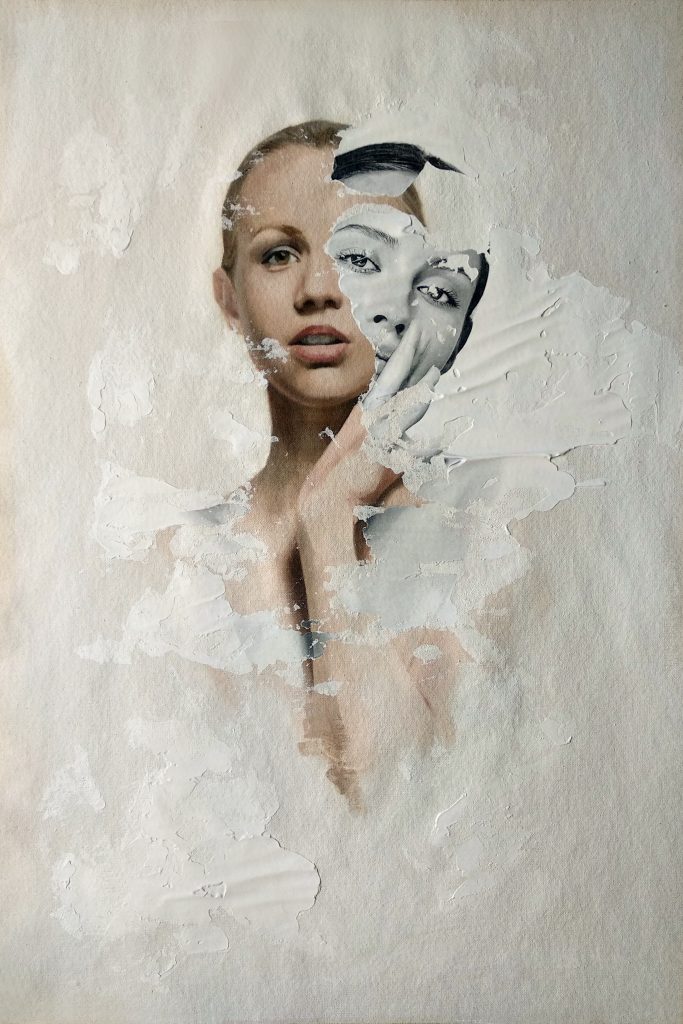
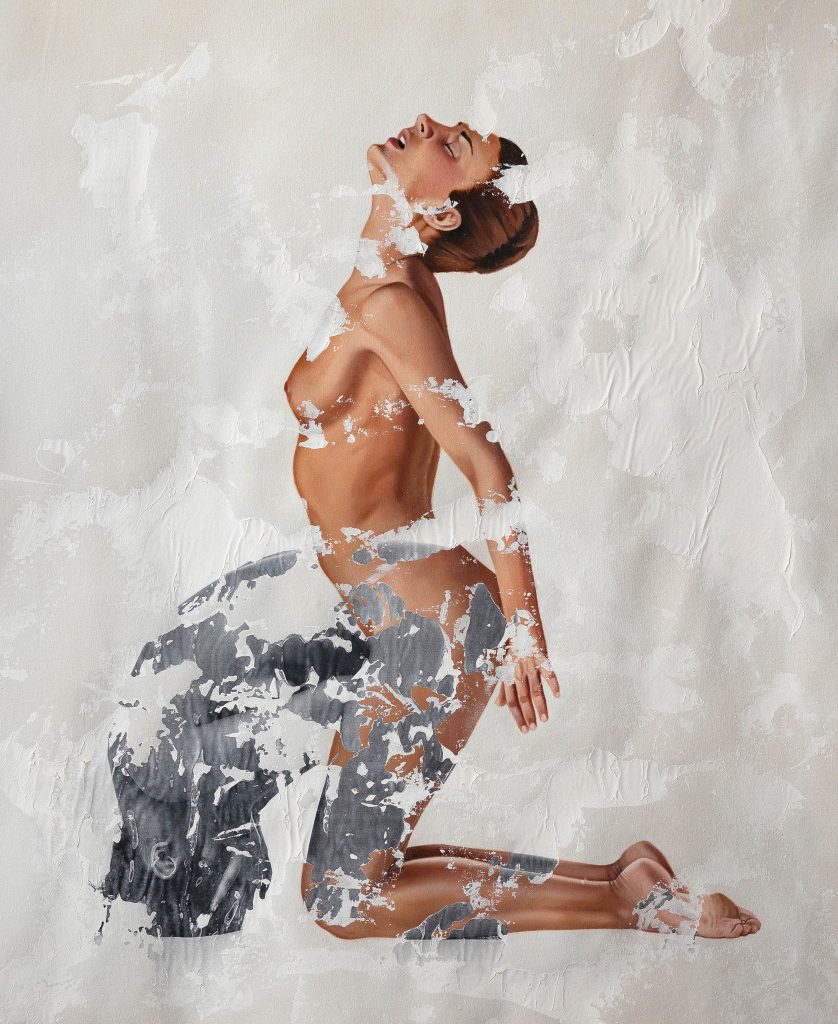
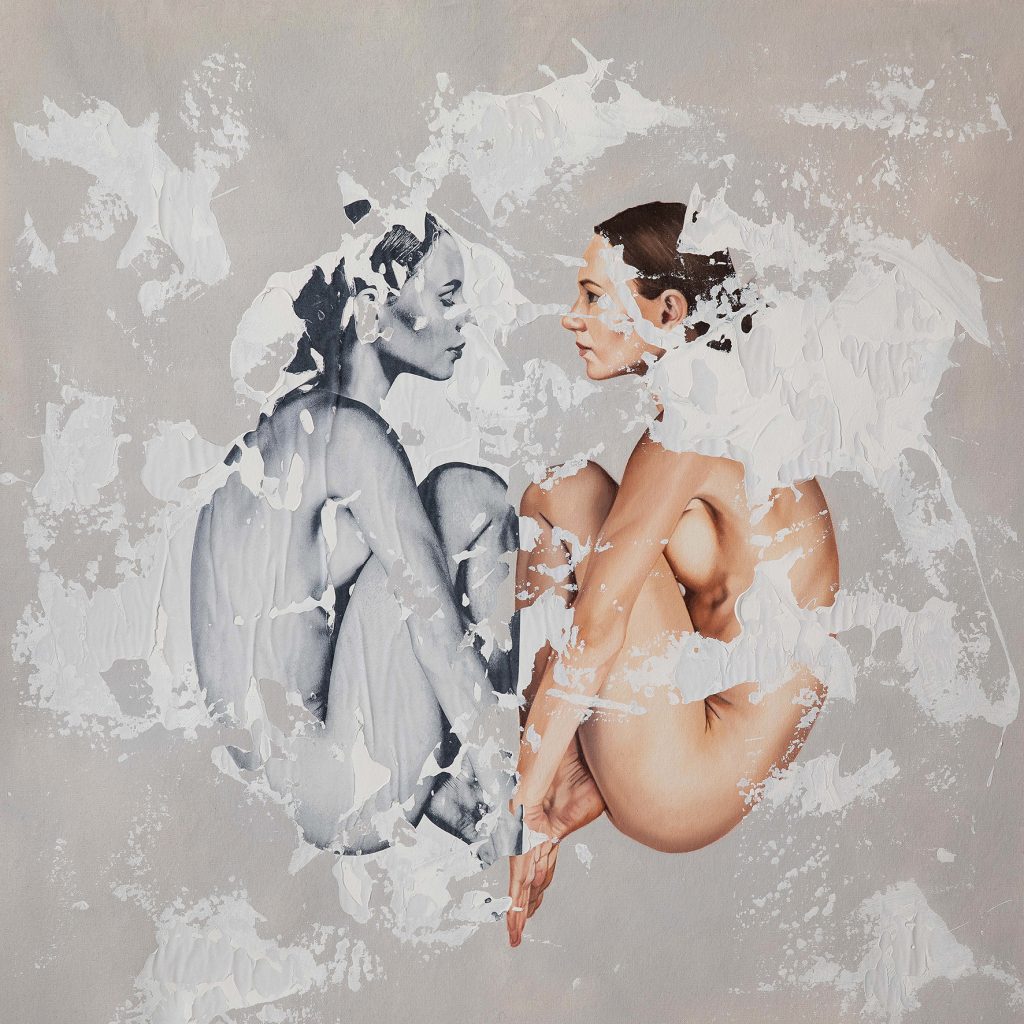
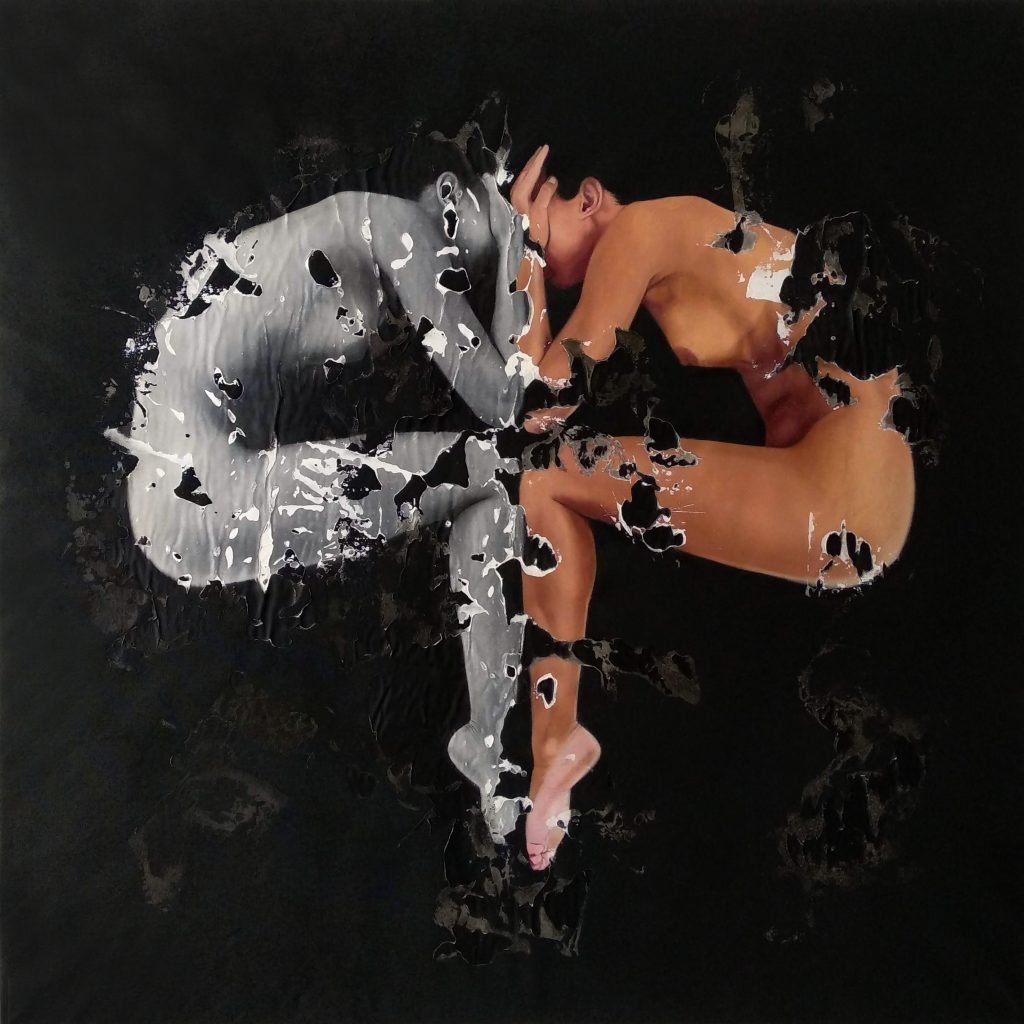










Conclusion
The creative process is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and creativity. By understanding the stages of the creative process and optimizing it through experimentation, collaboration, curiosity, embracing failure, and taking breaks, you can unlock your full creative potential.
FAQS
1. What is the Creative Process?
The creative process is a non-linear and iterative journey involving ideation, experimentation, and refinement. It begins with an idea or problem and concludes with a tangible solution or product.
2. What are the Four Stages of the Creative Process?
The creative process consists of four stages: Preparation, incubation, illumination and verification
3. How Can I Optimize the Creative Process?
To optimize the creative process, consider embracing failure as an opportunity to learn and grow, collaborate with others can generate new ideas and perspectives, taking breaks to refresh your mind and experimenting trying different techniques and approaches to generate fresh ideas.
4. Is the Creative Process Limited to Artists and Designers?
No, creativity is a skill that can be developed and applied in various fields. It’s not exclusive to artists and designers but can benefit professionals in diverse domains.