- Introduction
- What is Philosophical Art?
- Characteristics of Philosophical Art
- Exploring Major Movements in Philosophical Art
- Key Themes in Philosophical Art
- How to Interpret Philosophical Art
- Famous Examples of Philosophical Art
- Embracing Philosophical Art in Modern Culture
- The Impact of Philosophical Art
- The Future of Philosophical Art
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Have you ever wondered what makes some artworks so captivating and thought-provoking? How do they manage to convey complex and profound ideas through visual forms? What is the purpose and meaning behind these artistic expressions? If you are curious about these questions, you might be interested in exploring the fascinating world of philosophical art.
Philosophical art is a term that encompasses a variety of artworks that reflect, question, or challenge philosophical concepts and issues. In this article, we will dive into the depths of philosophical art and discover its characteristics, movements, themes, examples, and impact. We will also learn how to interpret and appreciate philosophical art, and how it relates to our modern culture and future.
What is Philosophical Art?
Philosophical art is a broad and somewhat ambiguous term that can have different interpretations depending on the context and perspective. However, a general definition of philosophical art is that it is art that engages with philosophy in some way. This can mean that the artwork:
- Expresses or illustrates a philosophical idea or theory
- Raises or explores a philosophical question or problem
- Critiques or challenges a philosophical doctrine or assumption
- Inspires or stimulates philosophical reflection or dialogue
Philosophical art is not limited to a specific medium, style, or genre. It can be found in painting, sculpture, photography, film, literature, music, and more. However, philosophical art is distinguished from other art forms by its emphasis on the intellectual and conceptual aspects of the artwork, rather than the aesthetic or emotional ones. Philosophical art is not meant to be merely beautiful or pleasing, but rather to provoke thought and discussion.
Philosophical art is also different from abstract art, which is art that does not represent or depict any recognizable objects or scenes. Abstract art can have philosophical implications, but it is not necessarily philosophical in itself. Philosophical art, on the other hand, can be realistic or abstract, but it always has a clear and intentional philosophical message or purpose.
Characteristics of Philosophical Art
Philosophical art can be identified by some common characteristics that distinguish it from other types of art. Some of these characteristics are:
- Symbolism and Allegory: Philosophical art often uses symbols and allegories to represent or suggest abstract or complex ideas. Symbols are objects, images, or signs that have a specific meaning or association, while allegories are stories or scenes that have a hidden or metaphorical meaning. For example, a skull can symbolize death or mortality, while a cave can allegorize ignorance or enlightenment.
- Depth of Emotional Impact: Philosophical art can have a profound emotional impact on the viewer, as it can evoke feelings of wonder, curiosity, confusion, awe, or even discomfort or distress. Philosophical art can challenge our assumptions, beliefs, and values, and make us question our own existence and reality. Philosophical art can also inspire us to seek deeper understanding and wisdom, and to appreciate the beauty and mystery of life.
- Challenging Perspectives: Philosophical art can offer alternative or unconventional perspectives on various topics and issues, such as morality, society, culture, religion, politics, science, and more. Philosophical art can expose the limitations or contradictions of our common sense or dominant views, and invite us to consider different or opposing viewpoints. Philosophical art can also encourage us to adopt a critical or reflective attitude, and to examine our own biases and prejudices.
Exploring Major Movements in Philosophical Art
Philosophical art has a long and rich history, spanning across different cultures and periods. Throughout history, many artists have been influenced by or engaged with philosophy, and have created artworks that reflect their philosophical interests and insights. Some of the most prominent movements in philosophical art are:


Surrealism
Emerging in the early 20th century, Surrealism was an artistic and literary movement influenced by Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theories and André Breton’s philosophical ideas. It aimed to express the unconscious mind and irrational human experience through artworks that combined reality and fantasy, logic and absurdity. Key artists included Salvador Dali, René Magritte, Max Ernst, and Frida Kahlo.
Existentialism
Developing in the mid-20th century, Existentialism was a philosophical movement influenced by Kierkegaard, Nietzsche, Sartre, and Camus. It focused on human freedom, responsibility, authenticity, and meaninglessness, exploring existential dilemmas and anxieties. Key artists associated with existentialism were Edvard Munch, Francis Bacon, Alberto Giacometti, and Samuel Beckett.
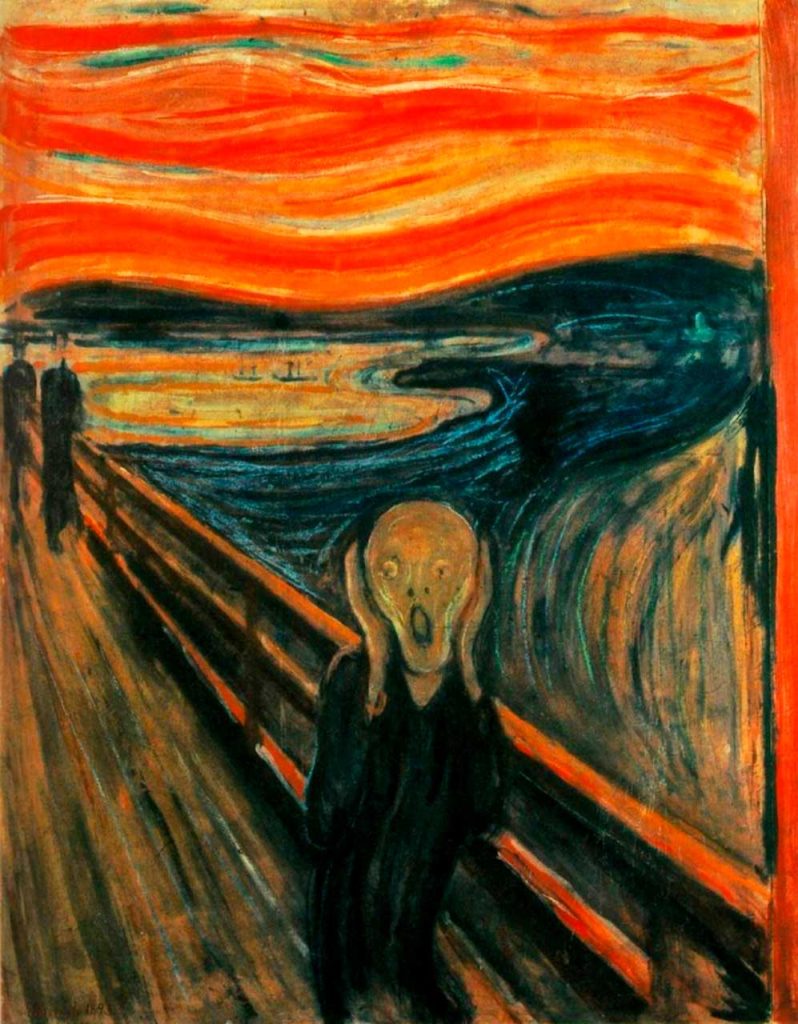




Symbolism
Originating in the late 19th century, Symbolism was an artistic and literary movement influenced by Schopenhauer, Schelling, and Baudelaire. It aimed to express spiritual and transcendental aspects of human experience, using symbols and metaphors to evoke emotions or states of mind. Key artists included Gustav Klimt, Odilon Redon, William Blake, and Edgar Allan Poe.
Key Themes in Philosophical Art


Philosophical art can address a wide range of themes and topics, depending on the artist’s intention and perspective. However, some of the most common and recurrent themes in philosophical art are:
- Existence and Meaning of Life: Philosophical art can explore the fundamental questions of human existence, such as: Who are we? Why are we here? What is the purpose of our lives? How do we find meaning and happiness? Philosophical art can also reflect on the existential challenges and crises that we face, such as: death, suffering, loneliness, absurdity, and nihilism.
- Perception and Reality: Philosophical art can question the nature and limits of our perception and knowledge of reality, such as: What is real? How do we know what is real? How do our senses, emotions, and thoughts shape our perception of reality? How do our language, culture, and society influence our understanding of reality? Philosophical art can also challenge our conventional or naive views of reality, and reveal the hidden or unknown aspects of reality, such as: illusions, paradoxes, mysteries, and secrets.
- Social and Political Issues: Philosophical art can comment on or critique the social and political issues and phenomena that affect our lives, such as: power, justice, equality, freedom, democracy, war, violence, oppression, and resistance. Philosophical art can also express or advocate for the social and political values and ideals that we aspire to, such as: peace, harmony, solidarity, diversity, and human rights.
How to Interpret Philosophical Art
Philosophical art can be challenging to interpret, as it often requires more than a superficial or literal reading of the artwork. Philosophical art can have multiple layers of meaning, and can invite different or even contradictory interpretations. However, there are some general steps that can help us to interpret and appreciate philosophical art, such as:
- Look beyond the surface: Philosophical art often uses symbolism and allegory to convey its message, so we need to look beyond the surface appearance of the artwork and try to identify the hidden or deeper meaning behind it. We can ask ourselves: What does this symbol or allegory represent or suggest? What is the artist trying to communicate or express through this symbol or allegory?
- Research the artist and their background: Philosophical art often reflects the artist’s personal or historical context, so we need to research the artist and their background to understand their inspiration, influences, and intended message. We can ask ourselves: Who is the artist and what is their biography? What are their philosophical interests and views? What are the historical and cultural circumstances that shaped their artistic vision and expression?
- Engage in personal reflection: Philosophical art often resonates with our own experiences and beliefs, so we need to engage in personal reflection to appreciate its emotional and intellectual impact. We can ask ourselves: How does this artwork make me feel or think? What does this artwork mean to me or relate to me? How does this artwork challenge or confirm my perspectives and understanding of the world?
Famous Examples of Philosophical Art


Philosophical art has produced some of the most famous and influential artworks in history, that have captivated and inspired generations of viewers and thinkers. Some of the most renowned examples of philosophical art are:
- Guernica: Guernica is a large-scale painting by Pablo Picasso, created in 1937, in response to the bombing of the Basque town of Guernica by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy during the Spanish Civil War. Guernica depicts the horrors and suffering of war, using a monochromatic palette and a distorted and fragmented style. Guernica is a powerful and poignant statement against war and violence, and a symbol of peace and humanity.
- The School of Athens: The School of Athens is a fresco painting by Raphael, created in 1509, as part of the decoration of the Vatican Palace. The painting depicts a group of ancient Greek philosophers and scholars, such as Plato, Aristotle, Socrates, and Pythagoras, engaged in dialogue and debate in a classical architecture. The painting is a tribute to the intellectual and cultural legacy of ancient Greece, and a reflection of the Renaissance humanist values and ideals.
- The Garden of Earthly Delights: The Garden of Earthly Delights is a triptych painting by Hieronymus Bosch, created in the late 15th or early 16th century. The painting depicts three scenes: the Garden of Eden, the Garden of Earthly Delights, and the Hell. The painting is a complex and mysterious allegory of human sin and folly, and the consequences of indulging in worldly pleasures and temptations. The painting is a rich and vivid source of symbolism and imagery, and a challenge to the viewer’s interpretation and imagination.
Embracing Philosophical Art in Modern Culture


Philosophical art is not a thing of the past, but a living and evolving phenomenon that continues to influence and inspire our modern culture. Some of the ways that philosophical art is embraced in our contemporary society are:
- Contemporary Artists Embracing Philosophy: Many contemporary artists are influenced by or engage with philosophy in their artworks, either by revisiting or reinterpreting the classical philosophical themes and movements, or by creating new and original philosophical expressions and perspectives. Some of the contemporary artists who embrace philosophy are Marina Abramović, Damien Hirst, Ai Weiwei, and Banksy.
- Impact on Society and Individual Perspectives: Philosophical art can have a significant impact on our society and individual perspectives, as it can raise our awareness and consciousness of the philosophical issues and challenges that we face in our modern world, such as: globalization, environmentalism, human rights, identity, and diversity. Philosophical art can also inspire us to seek and create positive change and transformation, and to cultivate our personal and collective values and ideals.
- The Intersection of Technology and Philosophical Art: Technology can play an important role in the creation and dissemination of philosophical art, as it can offer new and innovative ways of expressing and communicating philosophical ideas and messages. Technology can also enhance the accessibility and interactivity of philosophical art, as it can enable us to experience and participate in philosophical art through digital platforms and devices, such as: websites, social media, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
The Impact of Philosophical Art
Philosophical art can have a lasting and profound impact on our lives, as it can enrich and enlighten our minds and souls. Some of the benefits and effects of philosophical art are:
- It stimulates our curiosity and creativity: Philosophical art can spark our curiosity and creativity, as it can expose us to new and diverse ideas and perspectives, and challenge us to think outside the box and beyond the ordinary. Philosophical art can also encourage us to express our own thoughts and feelings, and to create our own artworks that reflect our philosophical vision and voice.
- It enhances our critical thinking and reasoning skills: Philosophical art can enhance our critical thinking and reasoning skills, as it can train us to analyze and evaluate the arguments and evidence presented in the artworks, and to identify the strengths and weaknesses of different philosophical positions and claims. Philosophical art can also help us to develop our own arguments and opinions, and to support them with logical and coherent reasoning and evidence.
- It fosters our emotional and moral development: Philosophical art can foster our emotional and moral development, as it can touch our emotions and sentiments, and make us empathize and sympathize with the experiences and values of others. Philosophical art can also help us to explore and understand our own emotions and values, and to cultivate our moral virtues and principles.
The Future of Philosophical Art


Philosophical art is not a static or fixed phenomenon, but a dynamic and evolving one, that adapts and responds to the changing times and circumstances. Some of the trends and movements that can shape the future of philosophical art are:
- Evolving Trends and Movements: Philosophical art can reflect the evolving trends and movements in philosophy, art, and culture, as it can incorporate and address the emerging and relevant topics and issues that affect our contemporary world, such as: artificial intelligence, biotechnology, neuroscience, and posthumanism. Philosophical art can also create and initiate new and original trends and movements, that can challenge and transform the existing paradigms and conventions in philosophy, art, and culture.
- Digital Platforms and Global Connectivity: Digital platforms and global connectivity can offer new and exciting opportunities and challenges for philosophical art, as they can enable the creation and dissemination of philosophical art across different media, formats, and genres, such as: podcasts, blogs, videos, and games. Digital platforms and global connectivity can also enhance the diversity and inclusivity of philosophical art, as they can allow the participation and collaboration of philosophical artists and audiences from different backgrounds, cultures, and locations.
- Shaping the Artistic Landscape Ahead: Philosophical art can play a significant role in shaping the artistic landscape ahead, as it can influence and inspire the future generations of artists and thinkers, and set the standards and criteria for artistic excellence and innovation, can also contribute to the advancement and enrichment of human civilization and culture, as it can promote and foster the values and ideals of wisdom, beauty, and truth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of philosophical art stands as a captivating and enriching domain of exploration and practice. It provides a profound avenue for gaining a more comprehensive understanding of philosophy, art, and life. Engaging with philosophical art has the potential to nourish our minds and souls, serving as a source of inspiration to instigate positive change and transformation in both ourselves and the world. We trust that this article has ignited your interest and curiosity in philosophical art, encouraging you to delve further into the diverse and remarkable works that await exploration and enjoyment.
FAQs
- What is philosophical art?
- Philosophical art is art that engages with philosophy in some way, such as expressing, questioning, or challenging philosophical concepts and issues.
- What are some characteristics of philosophical art?
- Some characteristics are symbolism and allegory, depth of emotional impact, and challenging perspectives.
- What are some movements in philosophical art?
- Some movements in philosophical art are surrealism, existentialism, and symbolism.
- What are some themes in philosophical art?
- Some themes in philosophical art are existence and meaning of life, perception and reality, and social and political issues.
- How can we interpret and appreciate philosophical art?
- We can interpret and appreciate philosophical art by looking beyond the surface, researching the artist and their background, and engaging in personal reflection.